Enthalpy of Atomization
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Enthalpy of Atomization
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we'll explore the concept of enthalpy of atomization, which is the energy needed to break the bonds of a compound completely to form gaseous atoms, right?

So, does that mean the enthalpy of atomization is the same for all molecules?

Good question! No, it varies. For diatomic molecules, such as H2, the enthalpy of atomization equals the bond dissociation enthalpy. For example, breaking H-H bond to form two H atoms requires 435 kJ/mol.

What about larger molecules? Do we calculate it differently?

Exactly! For larger molecules, each bond might have different energies. We sum up the energies required to break all the bonds to find the total enthalpy of atomization.

So, it's really about understanding how strong the bonds are between atoms, right?

Precisely! Stronger bonds require more energy, resulting in higher enthalpy of atomization. Remember, higher ΔaH° often correlates with less stability in those molecules.

Can we see an example of how this is used in reactions?

Certainly! We'll look into that as we proceed. A key point is that understanding enthalpy of atomization allows you to gauge the energy transfers in reactions.
Bond Dissociation and Enthalpy of Atomization
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s discuss bond dissociation energy and its relationship with enthalpy of atomization.

Is bond dissociation energy just another way to refer to enthalpy of atomization for diatomic molecules?

Exactly! For instance, when we dissociate H2 into two H atoms, the energy we measure is the same as the enthalpy of atomization.

And for larger molecules, how do we differentiate the bond energies?

In larger molecules, we would consider the individual bond energies for each bond, which may vary, and then sum them up to find the total heat of atomization.

Are there any practical applications for this concept?

Definitely! It helps in predicting reaction enthalpies and understanding stability, crucial in fields like materials science, pharmacology, and environmental chemistry.

So higher atomization energy generally means more unstable compounds?

That's right! Stability often correlates with lower enthalpy of atomization, which shows that strong bonds are harder to break.
Importance in Thermodynamics
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s dive into why understanding the enthalpy of atomization is essential in thermodynamics.

Does it affect the overall energy balance in a reaction?

Absolutely! The enthalpy of atomization can dictate the energy needed to drive reactions forward, influencing the feasibility and direction.

How does it compare with heat of formation?

Great point! The heat of formation assesses how energy changes when a substance forms from its elements, while enthalpy of atomization focuses on breaking bonds of existing compounds.

So, can we use these ideas in real-life situations like in designing new materials?

Exactly! Knowledge of bonds and energy changes informs everything from industrial polymer production to biofuel development.

This makes thermodynamics so relevant in our world today!

That's the spirit! Using these concepts, we can make predictions about materials and reactions based on their atomic and molecular structure.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section provides an overview of the enthalpy of atomization, explaining the enthalpy change associated with breaking chemical bonds to produce gaseous atoms. It elaborates on how this concept interacts with other thermodynamic principles, including bond dissociation enthalpy, and the application of these ideas in calculating the energy changes of chemical reactions.
Detailed
Enthalpy of atomization (ΔaH°) represents the energy change when one mole of a compound is converted into its constituent gaseous atoms. For diatomic molecules, the enthalpy of atomization is equivalent to the bond dissociation enthalpy, emphasizing the energy required to break the bond. This concept is essential in bond energy calculations, as it allows for the assessment of energy absorbed or released during chemical reactions.
In complex molecules, the enthalpy of atomization might differ from the mean bond enthalpy due to variations in bond energies among different atoms. The section connects enthalpy of atomization with thermodynamic laws, illustrating how it relates to stability and reactivity of compounds. Understanding this principle aids in predicting reaction behaviors and energy requirements, making it a cornerstone concept in thermodynamics and chemistry.
Youtube Videos
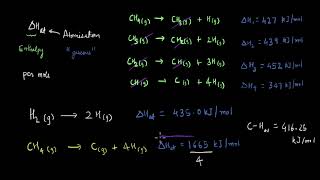





Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of Enthalpy of Atomization
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The enthalpy of atomization is defined as the enthalpy change that occurs when one mole of a substance is converted into gaseous atoms. It represents the energy required to break bonds in the substance and produce isolated gaseous atoms.
Detailed Explanation
The enthalpy of atomization quantifies the energy needed to convert a mole of a substance into its individual gaseous atoms. Essentially, it indicates how much energy must be supplied to overcome the forces holding the atoms together in the molecular structure. This is important in understanding chemical reactivity, as atoms tend to be more reactive in their gaseous state compared to their bonded form.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a tightly-packed crowd of people at a concert (the molecules in a gas). To get them to disperse and move freely (atoms in gas phase), you would need to apply some force (energy) to push them apart. The energy required to do this represents the enthalpy of atomization. For instance, breaking H-H bonds in hydrogen gas requires a specific amount of energy equivalent to its atomization enthalpy.
Examples of Enthalpy of Atomization
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
For diatomic molecules, such as hydrogen (H2), the enthalpy of atomization can be represented as:
H2(g) → 2H(g); ∆aH = +435 kJ mol–1
For polyatomic molecules like methane (CH4):
4CH4(g) → C(g) + 4H(g); ∆aH = 1665 kJ mol–1
Detailed Explanation
The examples illustrate that the enthalpy of atomization is different for different molecules. For diatomic hydrogen, the process of breaking the bond to create two hydrogen atoms (H) requires 435 kJ of energy. In contrast, for methane, where there are multiple bonds between carbon and hydrogen, breaking all the bonds to separate into individual atoms requires significantly more energy (1665 kJ). This difference underscores the impact of molecular complexity on energy requirements.
Examples & Analogies
Think of it as breaking down a Lego structure. For a simple two-piece Lego (like H2), it's easy to take apart, needing less effort (energy). However, for a larger, more complex Lego assembly with many pieces (like CH4), you would require more effort to take it apart. Each bond broken requires energy, just like separating the Legos requires physical force.
Importance in Chemistry
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Understanding enthalpy of atomization is crucial for predicting the behavior of molecules in reactions, particularly in determining the feasibility and stability of products formed during chemical processes.
Detailed Explanation
The enthalpy of atomization plays a vital role in chemical thermodynamics as it helps chemists to understand how bonds form and break during reactions. By knowing the enthalpy changes associated with the formation or breaking of specific bonds, scientists can predict the energy requirements for reactions and their spontaneity. This helps in designing reactions for synthetic processes and understanding reaction mechanisms.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you're trying to cook dinner – you need to know how long and at what temperature to prepare different dishes based on their ingredients. In chemistry, knowing the enthalpy of atomization is like a chef understanding the cooking time and method for various ingredients. If you understand how much energy (heat) is needed to break down or build up certain bonds, you can better plan your reaction process, much like a chef planning a meal.
Key Concepts
-
Enthalpy of Atomization: Measures the energy needed to form gaseous atoms from a compound.
-
Bond Dissociation Energy: The energy required to break specific chemical bonds.
-
Molecular Stability: Understanding how bond strength relates to the stability of a molecule.
Examples & Applications
The enthalpy of atomization for dihydrogen (H2) is equivalent to its bond dissociation energy, which is 435 kJ/mol.
In methane (CH4), the total enthalpy of atomization is calculated by summing the energies required to break all four C-H bonds.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
To break the bonds and make new gas, Atomization helps us, it's a must! Energy flows, that's a simple task, Enthalpy of our compound is the call we ask.
Stories
Imagine a castle (molecule) being torn down (broken apart) brick by brick (atom by atom), as each piece is pulled away, energy is required, illustrating the concept of enthalpy of atomization.
Memory Tools
Remember: 'A-B = Atomization, B-C′ when thinking about bonds being broken to create gaseous atoms.
Acronyms
B.E.S.T - Bond energy signifies the Enthalpy of gas formation when breaking Structure down.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Enthalpy of Atomization
The energy change required to break all the bonds in a compound to produce individual gaseous atoms.
- Bond Dissociation Enthalpy
The enthalpy change associated with breaking a specific bond in a molecule.
- Thermodynamics
The branch of physics that deals with energy and work, including the laws governing energy transfers.
- Molecular Stability
The tendency of a molecule to maintain its current structural arrangement without undergoing chemical change.
- Gaseous Atoms
Atoms that exist in the gas phase, free from intermolecular bonds.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
