Standard Enthalpy of Combustion
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Standard Enthalpy of Combustion
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we are going to explore standard enthalpy of combustion. Can anyone tell me what enthalpy means?

Isn't it about the heat content of a substance?

Exactly! Enthalpy represents the total heat content, especially during chemical reactions. Now, when we talk about standard enthalpy of combustion, it refers specifically to the heat released when one mole of substance burns completely in oxygen. It’s typically expressed in kJ/mol. Why do you think it’s important?

Because it tells us how much energy we can get from burning fuel?

Right! It helps in evaluating different fuels' efficiencies. Remember, the combustion of hydrocarbons is usually exothermic—that means it releases heat.
Applications of Combustion Enthalpy
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let's discuss where we see combustion enthalpy in action. Can anyone give me an example?

Like in cars! They burn gasoline, right?

Absolutely! The combustion process in engines is vital for vehicle operation. We also see it in household heating and electricity generation, especially with natural gas. What happens during the combustion process?

It produces carbon dioxide and water.

Correct! Combustion processes contribute significantly to overall energy output and understanding these processes is crucial for optimizing energy resources. An acronym to remember the combustion products is 'COW' for Carbon dioxide, Oxygen, and Water.
Calculating Enthalpy Changes
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s dive into how we compute the standard enthalpy of combustion. Who remembers Hess's Law?

It’s the law that states you can sum up the enthalpy changes of multiple steps to get the total change.

Exactly! If you know the combustion reactions of the reactants and products, you can sum their enthalpies to find the overall change. For example, what would be the reaction for burning butane?

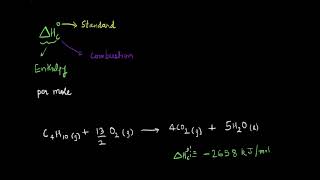
C₄H₁₀ + 6O₂ → 4CO₂ + 5H₂O.

Great! And when you look at the standard enthalpy values for each of those species, what would you do next?

Sum up the ΔH for products and subtract the ΔH of the reactants.

Correct! That gives us the standard enthalpy of combustion for butane. Remember, it’s essential to balance the chemical equation first!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section discusses the concept of standard enthalpy of combustion (∆cH°), its importance in various applications like energy generation, and how it can be calculated for different substances under standard conditions.
Detailed
Standard Enthalpy of Combustion
The standard enthalpy of combustion (∆cH°) is defined as the heat energy change when one mole of a substance undergoes complete combustion in oxygen, under standard state conditions. These conditions typically involve a temperature of 25 °C (298 K) and a pressure of 1 atm. This value signifies how much energy is released typically in the form of heat during the combustion reaction.
Significance of Combustion Enthalpy
- Energy Release: Combustion reactions are predominantly exothermic; thus, they release heat that can be harnessed for practical applications such as power generation and heating. For instance, the combustion of methane produces substantial energy, critical for everyday use in cooking and heating.
- Thermochemical Equations: The combustion enthalpy allows for the formulation of thermochemical equations, providing a thermodynamic perspective on energy changes in reactions involving fossil fuels, biofuels, or other hydrocarbons.
Examples and Calculation
Specific examples include the combustion of butane (C₄H₁₀) and glucose (C₆H₁₂O₆). For butane, the complete combustion yields carbon dioxide and water with a significant release of heat. The formula for calculating the standard enthalpy change can be derived from Hess’s Law of Constant Heat Summation. Each combustion reaction's stoichiometry is key to determining its associated enthalpy change.
In addition, knowing how to present these reactions in a standard format enhances our understanding of energy flows, enabling efficient designs for energy systems in various industries.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of Standard Enthalpy of Combustion
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Standard enthalpy of combustion (symbol: ∆cH0) is defined as the enthalpy change per mole (or per unit amount) of a substance, when it undergoes combustion and all the reactants and products being in their standard states at the specified temperature.
Detailed Explanation
The standard enthalpy of combustion refers to the amount of energy released when one mole of a substance is completely burned in oxygen under standard conditions (1 bar pressure and a specified temperature, often 298 K). It is an important measure in thermodynamics, especially for reactions where combustion occurs, because it helps in determining how much energy is produced from burning fuels. The standard state refers to the physical state of a substance under standard conditions, which allows for consistent comparisons.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine that burning a log in a fireplace releases heat to warm your home. If we know the standard enthalpy of combustion of that log, we can predict exactly how much heat it will release as it burns and how long it will keep the fire going.
Examples of Enthalpy of Combustion
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Cooking gas in cylinders contains mostly butane (C4H10). During complete combustion of one mole of butane, 2658 kJ of heat is released. Similarly, combustion of glucose gives out 2802.0 kJ/mol of heat.
Detailed Explanation
The example of butane shows that when one mole of butane is burned in the presence of oxygen, it releases a substantial amount of heat (2658 kJ). This can be utilized for cooking or heating. Similarly, glucose, a common source of energy in living organisms, releases even more energy (2802 kJ/mol) when it combusts. These values represent the standard enthalpy of combustion for butane and glucose, respectively, and highlight the amount of energy available from these fuels when they undergo combustion.
Examples & Analogies
Think of butane as the fuel in your gas stove. When you turn on the stove, butane burns, and the flame it produces is the result of that combustion releasing energy. The higher the enthalpy of combustion, the more heat you can generate—just like glucose is a high-energy compound that our bodies burn to fuel our activities.
Key Concepts
-
Standard Enthalpy of Combustion: Measures energy change during complete combustion reactions.
-
Exothermic Reactions: Reactions that release energy primarily as heat.
-
Combustion Products: Typically include carbon dioxide and water.
Examples & Applications
Specific examples include the combustion of butane (C₄H₁₀) and glucose (C₆H₁₂O₆). For butane, the complete combustion yields carbon dioxide and water with a significant release of heat. The formula for calculating the standard enthalpy change can be derived from Hess’s Law of Constant Heat Summation. Each combustion reaction's stoichiometry is key to determining its associated enthalpy change.
In addition, knowing how to present these reactions in a standard format enhances our understanding of energy flows, enabling efficient designs for energy systems in various industries.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In combustion, heat's the game, fuels provide it, that's the name!
Stories
Imagine a campfire where logs burn, releasing warmth and light—this is combustion!
Memory Tools
Fuels Go Hand in Hand: Fuel + O₂ = Heat + CO₂ + H₂O.
Acronyms
ABC - Always Burn Carbon
Refers to the burning of fuel in combustion reactions.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Enthalpy (H)
A measure of the total energy of a thermodynamic system, reflecting internal energy plus the energy associated with pressure and volume.
- Standard Enthalpy of Combustion (∆cH°)
The amount of energy released during the complete combustion of one mole of a substance at standard conditions.
- Exothermic Reaction
A chemical reaction that releases energy in the form of heat.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
