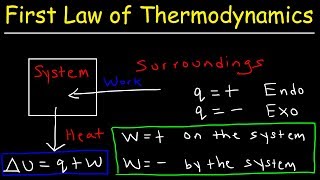
The system and the surroundings
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Systems and Surroundings
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we will explore the fundamental concepts of systems and surroundings in thermodynamics. Can anyone tell me what a thermodynamic system is?

Isn't a system the part of the universe we focus on for observations?

Great! That's correct. A system is indeed the focus of our study, while everything else is considered the surroundings. So, can anyone point out the difference between them?

The system is what we look at, and the surroundings include everything else that can interact with it.

Exactly! It’s crucial to understand these definitions because they help in categorizing systems into open, closed, and isolated types.

What do those terms mean?

An open system allows both energy and matter to exchange with its surroundings, like a beaker of water. A closed system allows energy transfer but not matter, like a sealed jar of gas. Finally, an isolated system does not exchange either with the surroundings, like a thermos.

So, the thermos keeps everything inside without outside interference?

Exactly! Now, let’s summarize these key points: a system is what we study, and the surroundings are everything else. We classify systems into open, closed, and isolated based on their interactions with the surroundings.
Types of Systems: Open, Closed, and Isolated
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we understand the basics, let's delve into the types of systems. What do you think makes an open system unique?

I think it can exchange both energy and matter!

Exactly! Open systems can interact freely with their surroundings, which can influence their energy states. How about a closed system?

It can exchange energy but not matter.

Correct! Think of a closed system like a pressure cooker; it can heat up the water inside but doesn't let any steam escape. And lastly, what's an isolated system?

It doesn't exchange anything with the surroundings!

Good job! Isolated systems are insulated from any forms of energy and matter exchange, like an insulated thermos. Let’s recap: open systems allow free exchange, closed ones can exchange energy only, and isolated systems don’t exchange anything.
Significance of Systems in Thermodynamics
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Why do you think understanding these system properties is essential in thermodynamics?

It helps predict how energy changes during reactions!

Exactly! Each type of system behaves differently under various conditions. For example, in open systems, reactions can change if we add heat or mix substances. What happens in isolated systems?

They maintain their energy and matter unless acted upon externally!

Correct! It’s critical for understanding energy conservation and transformation. Remember, thermodynamics helps us explain and predict the energy flow within chemical reactions and physical changes.

So understanding these systems gives us better control over reactions?

Exactly right! Understanding the system helps tailor reactions to achieve desired outcomes.

Let’s summarize today’s discussion: the classification of systems (open, closed, isolated) is crucial for predicting how they interact with their surroundings and how energy changes occur during chemical processes.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
In thermodynamics, the concepts of systems and surroundings are fundamental. The system refers to the part of the universe we focus on, while the surroundings encompass everything else that can interact with the system. Systems are categorized as open, closed, or isolated based on their ability to exchange matter and energy.
Detailed
In thermodynamics, understanding the distinction between 'the system' and 'the surroundings' is essential for analyzing energy changes during chemical reactions. The system is the specific part of the universe that is being studied, while the surroundings consist of everything that interacts with the system. Together, they make up the universe.
Systems can be categorized into three types:
1. Open System: Allows the exchange of both energy and matter with the surroundings, such as a beaker where reactants can interact with the air.
2. Closed System: Permits the exchange of energy but not matter, like a sealed container that can gain or lose heat but contains the same amount of substance.
3. Isolated System: Neither energy nor matter is exchanged with the surroundings, such as a thermos that keeps its contents insulated from outside temperature change.
Understanding these classifications helps scientists predict how energy changes during chemical processes, providing insights into the behavior of various systems within the field of thermodynamics.
Youtube Videos






Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Defining the System and Surroundings
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
A system in thermodynamics refers to that part of the universe in which observations are made and the remaining universe constitutes the surroundings. The surroundings include everything other than the system. System and the surroundings together constitute the universe.
Detailed Explanation
In thermodynamics, we divide the universe into two key parts: the 'system' and the 'surroundings'. The 'system' is the specific part we are focusing on, which could be a beaker with a chemical reaction occurring inside it. The 'surroundings' are everything else in the universe that is not part of the system but can interact with it. Together, they make up the entire universe, allowing us to study energy changes in a controlled manner.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you're baking a cake. The ingredients and the oven would be considered the system because that's what you're directly working with. Everything else in the kitchen—like the countertops, air, or even the fridge—is part of the surroundings. If something happens while baking, like the temperature changing in the oven, it affects the cake, representing how the system (cake) interacts with its surroundings (oven temperature).
Understanding Interaction with Surroundings
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
However, the entire universe other than the system is not affected by the changes taking place in the system. Therefore, for all practical purposes, the surroundings are that portion of the remaining universe which can interact with the system.
Detailed Explanation
While studying thermodynamics, it's important to note that not all parts of the surroundings are affected by what happens in the system. Only those parts that can exchange energy or matter with the system matter in our analysis. This helps simplify our observations because we can focus on the interactions that actually affect the system.
Examples & Analogies
Think about a pot of boiling water on a stove. The steam rising from the pot represents the system, while the surrounding air around it is part of the surroundings. The heat from the stove is what interacts with the pot and water to cause the boiling. If you were to measure the temperature of the air far away from the pot, you'd find it unchanged; this shows that not all parts of the surroundings are influenced by the system.
The Concept of Boundaries
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The boundary separates the system from the surroundings. This is designed to allow us to control and keep track of all movements of matter and energy in or out of the system.
Detailed Explanation
The boundary is crucial as it delineates the system from its surroundings. Boundaries can be physical (like walls of a beaker) or imaginary, helping us study the flow of energy and matter. Understanding where the system ends and the surroundings begin is essential for analyzing thermodynamic processes.
Examples & Analogies
If you think of a balloon filled with air, the balloon's material forms a boundary between the air inside and the external environment. You can observe how changes in temperature or pressure within the balloon (the system) can affect its shape without affecting nearby objects unless the boundary is breached, such as when it pops—demonstrating how boundaries keep systems distinct.
Example of a System in Action
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
For example, if we are studying the reaction between two substances A and B kept in a beaker, the beaker containing the reaction mixture is the system and the room where the beaker is kept is the surroundings.
Detailed Explanation
In a practical scenario, when two substances react in a beaker, the beaker, along with its contents (substances A and B), is classified as the system. The temperature of the room, the air, and everything else outside the beaker is considered the surroundings. This clear division helps us analyze the heat, work, and matter exchanges that occur during the reaction.
Examples & Analogies
Returning to our cake-baking example, if we think of the mixing bowl as the system, then the mixing bowl and cake batter are what's being observed. The oven's environment, such as the heat it generates, acts as the surroundings that influence the baking process, much like A and B in the chemistry example influence their reaction.
Key Concepts
-
System: Part of the universe being studied.
-
Surroundings: Everything outside the system that can interact with it.
-
Open System: Can exchange energy and matter.
-
Closed System: Can exchange only energy.
-
Isolated System: Cannot exchange energy or matter.
Examples & Applications
An open system example: A beaker of water exposed to air, allowing both evaporation (matter out) and temperature changes (energy out).
A closed system example: A sealed can of soda that allows pressure changes but does not permit gas escape.
An isolated system example: A thermos that retains heat and matter inside without any exchange with the environment.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In an open system, both things can flow, / Matter and energy, watch them go!
Stories
Imagine a beaker of water on a table, surrounded by air; that beaker can lose water vapors and absorb heat, illustrating an open system in action!
Memory Tools
Remember 'O-C-I': Open exchanges energy and matter, Closed is energy only, Isolated does neither.
Acronyms
SOCC
System
Open
Closed
Isolated - this helps remember the types of systems!
Flash Cards
Glossary
- System
The specific part of the universe being studied in thermodynamics.
- Surroundings
Everything external to the system that can interact with it.
- Open System
A system that can exchange both energy and matter with its surroundings.
- Closed System
A system that can exchange only energy, not matter, with its surroundings.
- Isolated System
A system that cannot exchange either energy or matter with its surroundings.
- Thermodynamics
The study of energy transformations and the laws governing such processes.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
