Thermodynamic Terms
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to the System and Surroundings
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's begin with the concept of thermodynamics! What do we mean by 'system' and 'surroundings' in thermodynamics?

Isn't the system just the part we're studying while the surroundings are everything else?

Exactly! The system is indeed the part of the universe where observations are made, while the surroundings include everything else. Together, they constitute the universe.

So if I'm studying a chemical reaction in a flask, the flask and contents are the system?

Very good observation! And everything around the flask, like the air and the table it's on, would be the surroundings.

Let’s summarize this: Remember, *the universe = system + surroundings.* Can anyone explain how a system can interact with its surroundings?

Like exchanging heat or matter?

Correct! Now let’s move to classifying different types of systems.
Types of Systems
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's classify systems further. Can anyone name the three types of systems in thermodynamics?

I think they are open, closed, and isolated systems.

That's right! Let's explore each type. First, an open system can exchange both energy and matter. Can anyone give an example?

A beaker with a chemical reaction happening inside, where gases can escape!

Excellent! Now, what about a closed system?

Maybe a sealed container where heat can escape but no matter can leave?

Exactly! Lastly, what do we mean by an isolated system?

Isn't that one where neither heat nor matter is exchanged?

Correct! An example is a thermos flask. Remember these types because they are fundamental in thermodynamic analysis!

Let's summarize the key points: An **open** system exchanges energy and matter, a **closed** system exchanges energy only, and an **isolated** system exchanges neither.
Internal Energy as a State Function
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s talk about internal energy, U. How do we explain this term?

Is it the total energy contained within the system considering all forms, like heat and chemical energy?

Yes! Internal energy includes all forms of energy within a system. It changes primarily due to heat exchange, work done, or matter exchanged. What do we know about it being a state function?

It means its value depends only on the current state, not on how we got there!

Exactly right! This is crucial when analyzing thermodynamic changes. So if U = U_final - U_initial, what does it mean for a process?

It shows that the change in internal energy is determined by the states of the system rather than the process taken!

Great job! To recap, internal energy is a state function that represents the total energy of a system, and it changes based on heat, work, or matter exchange.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
An overview of thermodynamics, this section explains crucial concepts including the definitions of system and surroundings, and classifies systems into closed, open, and isolated types. It also introduces internal energy as a state function, detailing how it can change through heat and work, while emphasizing the implications of state functions in thermodynamic processes.
Detailed
Thermodynamic Terms
This section explores the foundational terms of thermodynamics vital for understanding energy transformations in physical and chemical processes. A system in thermodynamics refers to a specific part of the universe where observations are made, with everything outside the system being termed the surroundings. Together, the system and surroundings form the universe.
The section categorizes systems into three types:
1. Open System: Exchanges both energy and matter with its surroundings.
2. Closed System: Exchanges energy but not matter.
3. Isolated System: Exchanges neither energy nor matter.
Furthermore, the internal energy (U) of a system encompasses all kinds of energy within, such as chemical and mechanical energy. Internal energy is crucial as it changes when heat enters or exits the system, work is performed on or by the system, or when matter is exchanged. It is classified as a state function since its value depends only on the current state of the system, not the path taken to reach that state. Understanding these concepts is crucial for analyzing processes in thermodynamics, leading to deeper explorations of work, heat, and energy balance.
Youtube Videos






Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
System and Surroundings
Chapter 1 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
A system in thermodynamics refers to that part of the universe in which observations are made and remaining universe constitutes the surroundings. The surroundings include everything other than the system. System and the surroundings together constitute the universe. The universe = The system + The surroundings. However, the entire universe other than the system is not affected by the changes taking place in the system. Therefore, for all practical purposes, the surroundings are that portion of the remaining universe which can interact with the system. Usually, the region of space in the neighbourhood of the system constitutes its surroundings. For example, if we are studying the reaction between two substances A and B kept in a beaker, the beaker containing the reaction mixture is the system and the room where the beaker is kept is the surroundings. The boundary that separates the system from the surroundings is called the boundary. This is designed to allow us to control and keep track of all movements of matter and energy in or out of the system.
Detailed Explanation
In thermodynamics, the universe is divided into two parts: the system, which is the focus of our study (e.g., the contents of a beaker where a chemical reaction occurs), and the surroundings, which is everything else that can interact with the system, such as the air and the table where the beaker is placed. The boundary separates these two zones. Understanding this separation helps us analyze how energy and matter are transferred during reactions. If we look at a beaker with two chemicals in it, we consider only what happens inside that beaker (the system) while everything outside (like the air around it) is considered the surroundings.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the system as a small fenced area in a garden where you are planting flowers (your chemical reactions), while the rest of the garden, which is open and contains more plants, tools, and paths, is the surroundings. You focus only on your flowers and how they interact with the soil and sunlight, while the rest of the garden can still affect your activities without being the primary focus.
Types of Systems
Chapter 2 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
We further classify the systems according to the movements of matter and energy in or out of the system. 1. Open System: In an open system, there is exchange of energy and matter between the system and surroundings. For example, a beaker of water with ice cubes in it represents an open system. 2. Closed System: In a closed system, there is no exchange of matter, but exchange of energy is possible between system and the surroundings. An example is a sealed container of gas that can transfer heat but doesn't allow gas to escape. 3. Isolated System: In an isolated system, there is no exchange of energy or matter between the system and the surroundings. A thermos flask is an example of an isolated system.
Detailed Explanation
Understanding the different types of systems helps us analyze energy changes effectively. An open system allows both heat and matter to move across the boundary, such as when boiling water, where steam escapes. A closed system can exchange energy (like heat) but not matter (like a sealed can of soda that can get hot but doesn't lose any liquid). Lastly, an isolated system does not exchange energy or matter with its surroundings, resembling a well-insulated thermos that keeps hot soup hot without anyone feeling the warmth outside it.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine cooking: when you boil pasta in an open pot (open system), steam escapes into the air. If you put a lid on it but keep the heat on (closed system), the water can't escape, but it can still get hot. In contrast, a thermos (isolated system) keeps hot soup hot without letting any heat escape, as if it’s in its own little world.
The State of the System
Chapter 3 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The system must be described in order to make any useful calculations by specifying quantitatively each of the properties such as its pressure (p), volume (V), and temperature (T) as well as the composition of the system. We need to describe the system by specifying it before and after the change. The state of a thermodynamic system is described by its measurable or macroscopic (bulk) properties. Variables like p, V, T are called state variables or state functions because their values depend only on the state of the system and not on how it is reached.
Detailed Explanation
A thermodynamic system's state is characterized by its properties—pressure, volume, and temperature—which shape how it behaves during processes like heating or cooling. Specifying these values allows for calculations of energy changes, such as how much work a given amount of gas can do when it expands. Importantly, these state functions (pressure, volume, temperature) are defined independently of the path taken to reach them; only the initial and final states matter.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a car's journey: the car's current speed (velocity), the amount of fuel left (volume), and the engine's temperature (heat) represents its state at any moment. It doesn’t matter whether the car got there from a long highway drive or by navigating through a slow city street; only those three characteristics summarize its current performance.
Internal Energy as a State Function
Chapter 4 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
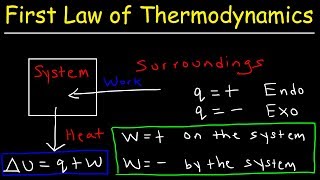
The total energy of the system, which we refer to as internal energy (U), can change when heat passes into or out of the system, work is done on or by the system, or matter enters or leaves the system. We express this internal energy mathematically as: ∆U = q + w, where q represents heat and w represents work. Internal energy, U, of the system is a state function, meaning it only depends on the current state of the system.
Detailed Explanation
Internal energy is an essential concept in thermodynamics, representing the total energy stored within a system. When energy transfers occur as heat (q) or work (w), the total internal energy changes. Understanding how these energy changes occur means assessing other energies (like heat or work) as merely mechanisms to change the internal energy. Because internal energy is a state function, knowing its final value is sufficient—it doesn't matter how it reached that point, simplifying calculations for energy transformations.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a bank account representing a person's finances: the account balance shows how much money is available (internal energy), while deposits and withdrawals represent heat and work. The total money can change with each transaction (heat in/out, work done), but knowing the current balance is enough to understand their financial state without needing to track every individual transaction.
Heat and Work in Changing Internal Energy
Chapter 5 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Heat can change the internal energy of a system without doing work, as seen in conditions where the system allows heat transfer (e.g., a pot of water on a stove). However, work done on a system also influences internal energy, as in the case of compressing gas in a piston.
Detailed Explanation
In thermodynamics, heat and work are two primary means through which internal energy changes. Heat relates to energy transfer due to temperature differences, while work pertains to energy transfer through actions such as pushing or compressing a gas. Recognizing how heat and work contribute to the total energy change of a system allows chemists to predict how various processes will affect internal energy.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a balloon: if you heat it up (adding heat), the gas inside expands, increasing the internal pressure without physically pushing it (no work done). On the other hand, when you squish it down (doing work), you also change the internal energy within the balloon. Each interaction gives you insights into how energy is stored and transferred.
Key Concepts
-
System and Surroundings: The system is what we observe, and surroundings are everything else.
-
Types of Systems: Systems can be open, closed, or isolated, reflecting how they interact with their surroundings.
-
Internal Energy: Internal energy is the total energy of a system and a state function, indicating its independence from the process followed.
Examples & Applications
An open system example is a chemical reaction occurring in an open beaker, allowing exchanges of gases with its surroundings.
A closed system example is a reaction inside a sealed container that retains its matter but allows heat exchange.
An isolated system example is a food thermos that maintains temperature by not allowing heat transfer.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In thermodynamics, systems are here, / Open, closed, isolated - crystal clear, / Surrounding everything near!
Stories
Imagine a sealed jar with jellybeans (the system) inside. The jar interacts with kids around it (the surroundings). If the jar is cracked open, kids can take jellybeans out (open system); if it’s taped but no air can come in, it’s closed; if it’s wrapped tightly, it’s isolated.
Memory Tools
Remember the acronym S.O.C. for System, Open, Closed – as a reminder of the basic definitions.
Acronyms
U.E.S. - U for Internal Energy, E for Energy Exchange, S for Systems definition.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- System
A part of the universe under observation, which can exchange energy or matter with its surroundings.
- Surroundings
Everything outside the system that can interact with it.
- Open System
A system that can exchange both energy and matter with its surroundings.
- Closed System
A system that can exchange energy but not matter with its surroundings.
- Isolated System
A system that cannot exchange either energy or matter with its surroundings.
- Internal Energy (U)
The total energy within a system, including all forms of energy.
- State Function
A property whose value depends only on the state of the system and not on how it reached that state.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
