AWT Hierarchy
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to AWT Hierarchy
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're going to explore the AWT hierarchy, a foundational concept in GUI programming with Java.

What do you mean by AWT hierarchy?

Great question! The AWT hierarchy shows how different classes relate to each other, starting from the `Object` class at the top, down to various GUI components like `Container`, `Component`, and others.

So, `Object` is the base for everything in Java?

Exactly! This is a good mnemonic: 'All Java objects come from `Object`, just like roots of a tree.' The hierarchy grows downwards from there.

What are Components and Containers?

Components are the visual elements, like buttons and labels, while Containers are used to hold these Components, like `Panels` or `Frames`.

Can containers hold other containers?

Yes, they can. Containers can indeed contain other containers to create complex layouts, enhancing GUI organization.

To summarize, the AWT hierarchy starts with `Object`, then `Components`, and organizes them using `Containers`.
Understanding Components
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we understand the hierarchy's basic structure, let’s dive deeper into `Component` classes.

What kinds of components can we use in AWT?

AWT offers various components like `Button`, `Label`, and `TextField`. They are all subclasses of the `Component` class.

And what about the `Container` class?

The `Container` class extends `Component` and can hold multiple components. Examples include `Panel`, `Frame`, and `Dialog`.

Can you name some specific functions of these containers?

Certainly! For example, `Frame` presents the main window of an application, while `Panel` can be used to group components.

So, all these classes have specific roles in the hierarchy?

Absolutely! Each component and container serves a purpose in building a complete GUI application.

In summary, we have `Component` classes, which are visual elements, and `Container`, which organizes them.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section examines the AWT class hierarchy, detailing the primary classes including Object, Component, and Container, which are fundamental for building graphical user interfaces in Java.
Detailed
AWT Hierarchy Overview
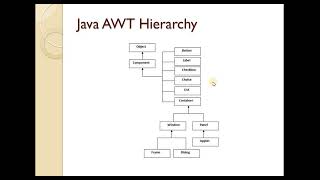
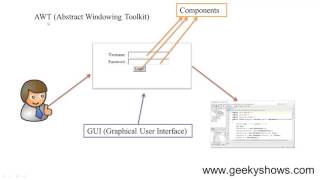
The AWT (Abstract Window Toolkit) is Java's original GUI toolkit, establishing the groundwork for creating graphical interfaces. The AWT hierarchy is organized around the Object, Component, and Container classes, forming a tree structure that defines the relationship between various GUI elements. At the top is the Object class, which serves as the root for all classes in Java. Below this, Component represents any visual object within a GUI. Finally, the Container class further expands on this by organizing visual components into logical groups, with specific subclasses like Window, Frame, Dialog, and Panel, each serving unique purposes in GUI structure. Understanding this hierarchy is crucial for effective GUI programming in Java, as it establishes the relationships and roles of different components.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Core Object in AWT
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Object
└── Component
Detailed Explanation
In the AWT hierarchy, 'Object' is the base class (the topmost element) in Java. From 'Object', we derive 'Component', which represents any visible element that can be displayed on the screen. The 'Component' class is a fundamental part of AWT, as all visual items (like buttons, labels, etc.) must extend this class to be recognized as GUI components in the framework.
Examples & Analogies
Think of 'Object' as the general category of things in a library, and 'Component' as a specific type of item — say, books — available in that library. Just like every book must belong to the library, every visible element in a GUI must be a component.
Containers in AWT
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
└── Container
├── Window
│ ├── Frame
│ └── Dialog
└── Panel
Detailed Explanation
In AWT, 'Container' is an important subclass of 'Component' that can hold other components. This means that containers can contain other visible elements, which allows for more complex layouts. 'Window' is a primary type of container that represents a top-level window in AWT. Inside 'Window', we have 'Frame' (a standard window that can have title bars and other decorations) and 'Dialog' (a pop-up window that typically requires user interaction). Additionally, 'Panel' is a more versatile container used to organize components in a window or frame.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a house as a 'Container' where you can place various rooms (like 'Window', 'Frame', and 'Dialog'). Each room may have different purposes and layouts, just like a frame can display information and a dialog box can request user input. The panel functions like a storage area in the house, grouping various items (components) together for better organization.
Key Concepts
-
AWT hierarchy: The structure of GUI classes in Java, starting with Object.
-
Component: An individual GUI visual element, such as buttons or labels.
-
Container: A class that holds other components to organize them in the GUI.
Examples & Applications
The Button class represents a clickable button in an AWT interface.
The Frame class creates the main application window where other components can be placed.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In AWT's tree, Objects rise, Components, Containers, a sweet surprise.
Stories
Imagine a tree called AWT - The Object is the trunk, strong and sturdy. Branching out are Components like Buttons and Labels, with Containers like Frames holding them safe and secure.
Memory Tools
Remember: O, C, Co - Object, Component, Container in AWT.
Acronyms
AC - All Components (under Container) show the hierarchy in a glance!
Flash Cards
Glossary
- AWT
Abstract Window Toolkit; Java's original GUI toolkit that provides a set of APIs for building graphical user interfaces.
- Component
An elemental visual part of a GUI, such as buttons or text fields, that is represented by a class.
- Container
A special type of component that can hold multiple other components, such as frames or panels.
- Object
The root class in Java from which all other classes inherit.
- Frame
A type of container that provides a main window for an application.
- Panel
A container that can hold a group of components for organization.
- Dialog
A pop-up window that prompts the user for input or presents information.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
