Layout Managers in Swing
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Layout Managers
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're going to explore Layout Managers in Swing, which help us arrange components like buttons and text fields within our GUI. Can anyone tell me what they think a layout manager does?

Is it like organizing furniture in a room?

That's a great analogy! Just like arranging furniture, layout managers organize components. They dynamically adjust how elements look when the window resizes.

What are some examples of layout managers?

We have FlowLayout, BorderLayout, GridLayout, and CardLayout in Swing, among others. Each serves unique purposes. Let's remember 'FBGC' for these!
Different Types of Layout Managers
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we know some layout managers, can anyone explain how GridLayout works?

I think it arranges components in a grid format?

Exactly! It creates a grid in which components are laid out in rows and columns. Can anyone think of situations where this could be useful?

Maybe in a form with multiple input fields?

Right! Now let’s summarize what we've learned. Layout managers control how components are displayed, like furniture in a styled room, making your application flexible.
Advanced Layout Management
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's discuss some advanced layout managers, specifically GroupLayout. Who can tell me what makes it different?

Isn't it for more complex layouts?

Exactly! GroupLayout allows for better control over component positioning. It can align components both horizontally and vertically. Think of it like a team working together in groups!

Can it be used for dynamic layouts?

Yes! It is especially useful for responsive designs. Now, remember 'Simple Layout = Layout Manager' for the basic concept!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Layout managers organize the placement of components within a container in Swing, extending those found in AWT, including GroupLayout and SpringLayout. They enhance GUI design by managing how components are laid out responsively.
Detailed
Layout Managers in Swing
In Swing, layout managers serve a crucial function by controlling the placement and sizing of components within a container. They ensure that components are arranged in a way that is visually appealing and functional, adhering to responsive design principles. Similar to AWT, Swing retains the same core layout managers like FlowLayout, BorderLayout, GridLayout, and CardLayout but also includes additional layouts such as GroupLayout and SpringLayout, enabling more complex arrangements.
Importance
Layout managers allow developers to maintain a consistent look and feel across different screen sizes and resolutions, resolving common issues associated with fixed positioning in GUIs. With the use of layout managers, developers can create interfaces that adaptively adjust to accommodate various elements as they are resized or as more components are added.
Youtube Videos






Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Overview of Layout Managers
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Same as AWT (Swing extends AWT containers).
Detailed Explanation
In Swing, layout managers serve the same purpose as those in the AWT framework. They provide a way to arrange and resize GUI components automatically. Since Swing is built on top of AWT, it inherits these layout management functionalities but adds its own enhancements. Layout managers handle the positioning and sizing of components in a user-friendly way, ensuring they scale properly across different screen sizes.
Examples & Analogies
Think of layout managers like the planning of furniture in a room. Just as a good layout can optimize the use of space and make the room comfortable and functional, layout managers help in organizing components in a GUI application so that they fit nicely within the application window.
Additional Layout Managers
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Additional: GroupLayout, SpringLayout, etc.
Detailed Explanation
In addition to the traditional layout managers found in AWT, Swing also offers more advanced layout managers like GroupLayout and SpringLayout. GroupLayout allows for a flexible arrangement of components, accommodating different sizes and alignments, which is particularly useful in more complex interfaces. SpringLayout lets developers specify constraints for components based on the position and size of other components, providing precise control over the GUI's appearance.
Examples & Analogies
If you consider a professional interior designer who can arrange furniture by focusing on the relationships between pieces (like how a couch should be positioned in relation to a coffee table), this is akin to what GroupLayout and SpringLayout do in a GUI, allowing for deeper control over component arrangements than basic layouts do.
Key Concepts
-
Layout Managers: Essential for arranging components in a GUI.
-
FlowLayout: Arranges components in a line; wraps when the line is full.
-
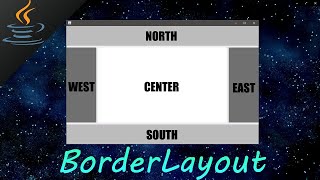
BorderLayout: Organizes interface parts into five predefined areas.
-
GridLayout: Uses a grid pattern for component placement.
-
CardLayout: Manages multiple components as 'cards' that can be navigated.
Examples & Applications
Using FlowLayout to arrange buttons in a toolbar.
Implementing BorderLayout to create a frame with a header, footer, and side menus.
Employing GridLayout for a calculator interface.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In Grid we fit, in Flow we flow, with Border in place, our layout will glow.
Stories
Imagine a town square (BorderLayout) with shops at the corners and a park in the middle. People flow in and out (FlowLayout), arranging themselves nicely (GridLayout), while groups of friends sit together (GroupLayout).
Memory Tools
Remember 'FBGC' for the main layout managers: Flow, Border, Grid, Card.
Acronyms
LAYOUT = Layout, Arrangement, Your, Organization, Understand, Try!
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Layout Manager
An object in Swing that arranges components within a container in a specific layout.
- FlowLayout
A layout manager that arranges components in a left-to-right flow, similar to lines of text.
- BorderLayout
A layout manager that divides the container into five areas: north, south, east, west, and center.
- GridLayout
A layout manager that places components in a rectangular grid with specified rows and columns.
- CardLayout
A layout manager that displays one component at a time, useful for switching between different views.
- GroupLayout
A layout manager that allows components to be grouped and aligned similarly, enabling sophisticated layouts.
- SpringLayout
A layout manager that allows components to be resized and positioned relative to each other.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
