Common Event Listener Interfaces
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Event Listener Overview
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we are going to discuss event listeners in GUI programming. Can anyone tell me what an event listener is?

Is it something that waits for user actions, like mouse clicks?

Exactly! Event listeners are interfaces that allow your program to respond to user actions. They capture events and allow us to perform actions when those events occur.

What are some examples of events we can listen for?

Great question! Common events include button clicks, mouse movements, key presses, and window actions. Each of these events is handled by a specific listener interface.

Just remember the acronym AMKW for ActionListener, MouseListener, KeyListener, and WindowListener to help you recall these common interfaces.

To summarize, event listeners are crucial for making our applications interactive, allowing us to respond to user input effectively.
ActionListener
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let's explore the ActionListener interface. Who can explain what this interface is used for?

I think it’s used for handling button clicks?

Correct! The ActionListener interface is specifically designed for responding to action events, primarily from buttons. For instance, we use it to execute code when a button is pressed.

Can you show us how it works?

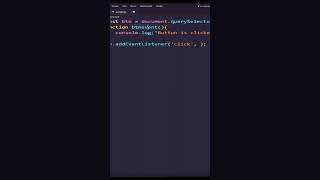
"Sure! Here's a simple example:
MouseListener and MouseMotionListener
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Next, we have MouseListener and MouseMotionListener. What do you think these interfaces handle?

I think they handle mouse actions like clicks and movements?

That's right! MouseListener captures events like mouse clicks and button state changes, while MouseMotionListener tracks mouse movements and drags.

Can you give us some examples of how we would use them?

Certainly! For example, by implementing MouseListener, we can change the color of a button when it's clicked or hovered over. Similarly, with MouseMotionListener, we can track the mouse's position and display coordinates on the screen.

For memory, think 'Mouse = Move' to remember both listener roles!

In conclusion, these interfaces help us create more interactive and engaging applications by responding to mouse actions.
KeyListener and WindowListener
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Finally, let’s discuss KeyListener and WindowListener. What do you think these listeners do?

KeyListener probably handles keyboard inputs, right?

Correct! KeyListener allows our application to respond to keystrokes, such as detecting when keys are pressed or released.

And what about WindowListener?

WindowListener manages events related to window actions like opening, closing, minimizing, or maximizing the window. It’s crucial for handling the application's lifecycle.

To remember, think 'Keyboard = KeyListener' and 'Window = WindowListener'.

Overall, understanding these event listeners allows us to build responsive GUI applications that enhance user engagement.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
In this section, we explore the various event listener interfaces that are essential for processing events in GUI applications. Key interfaces include ActionListener for button clicks, MouseListener and MouseMotionListener for mouse events, KeyListener for keyboard inputs, and WindowListener for window events, emphasizing their roles in enhancing user experience.
Detailed
Common Event Listener Interfaces
In GUI programming, event listeners are critical for responding to user interactions. This section outlines some of the most commonly used event listener interfaces in Java's AWT and Swing GUI frameworks:
- ActionListener: Handles action events, primarily used for button clicks. For example, implementing
ActionListeneron a button allows the program to execute a specific action when the button is clicked.
- MouseListener: Captures mouse events, including clicks, presses, and releases. It allows for interactive feedback based on mouse movements.
- MouseMotionListener: Extends the
MouseListenerfunctionality to monitor mouse drag and movement events. - KeyListener: Listens to keyboard events, enabling programs to respond to keystrokes from the user.
- WindowListener: Monitors window events, such as opening or closing a window, crucial for managing application state.
Each of these interfaces plays a vital role in making GUI applications interactive, improving user experience and engagement. Understanding how to implement these listeners creates a responsive GUI that reacts appropriately to user input.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Event Listeners Overview
Chapter 1 of 1
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Event Interface
- Button click
ActionListener - Mouse events
MouseListener,MouseMotionListener - Key press
KeyListener - Window open/close
WindowListener
Detailed Explanation
This chunk provides a list of the common event listener interfaces used in Java GUI programming. An 'event listener' is a piece of code that listens for specific actions (events) triggered by user interactions with GUI components. Each type of action corresponds to a specific interface:
- ActionListener: Used for listening to button clicks. When a button is clicked, the actionPerformed method in this listener is called.
- MouseListener: This interface is for mouse events like clicks and movements. It has several methods to handle different mouse actions.
- MouseMotionListener: This is a subset of MouseListener that specifically deals with mouse movements.
- KeyListener: Used for listening to keyboard events, such as key presses and releases.
- WindowListener: This interface handles events related to the window, such as opening and closing the window.
Examples & Analogies
Think of event listeners like a waiter in a restaurant. Just as the waiter listens for customers' orders (events) and acts upon them (serving food), event listeners wait for user interactions with GUI components (like clicking buttons or typing) and respond accordingly. For example, when you click a button to submit an order, the ActionListener acts like the waiter taking your order and processing it through the kitchen.
Key Concepts
-
Event Listener: An interface used to capture and handle events generated by user interactions.
-
ActionListener: Specifically responds to action events like button clicks.
-
MouseListener: Listens for mouse events such as clicks and drags.
-
KeyListener: Monitors keyboard actions, allowing reactions to key presses.
-
WindowListener: Handles events related to window management.
Examples & Applications
Using ActionListener to handle button clicks in a Swing application, allowing users to interact with buttons effectively.
Implementing MouseListener to change the color of a panel when the mouse hovers over it, providing visual feedback.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
For every button click or tick, ActionListener will do the trick.
Stories
Imagine a busy restaurant where a waiter listens for orders (ActionListener) at the click of buttons (tables) and attends to customers' movements (MouseListener) as they roam about, ensuring the perfect dining experience!
Memory Tools
Use AMKW: Action for buttons, Mouse for clicks, Key for typing, and Window for windows!
Acronyms
AMKW
ActionListener
MouseListener
KeyListener
WindowListener.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- ActionListener
An interface that handles action events, primarily used with buttons in GUI applications.
- MouseListener
An interface that listens to mouse events including clicks, presses, and releases.
- MouseMotionListener
An interface that tracks mouse moving and dragging events.
- KeyListener
An interface that listens to keyboard events like key presses and releases.
- WindowListener
An interface that handles window-related events such as opening, closing, or resizing.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
