JavaFX Architecture
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
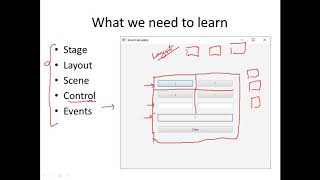
Stage Component
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's start with the Stage in JavaFX. The Stage is the main window of a JavaFX application. Can anyone tell me what they think it represents?

I think it's like the frame of a painting where everything is displayed.

Exactly! You can think of the Stage as the canvas for your application. Can someone explain its relationship with scenes?

So, a Stage can hold different scenes, kind of like different views?

Correct! You can switch scenes on a stage based on user actions. Remember, Stage is what users see first. Let's move to Scenes.
Scene Component
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

As mentioned, a Scene is the content within a Stage. Who can give me an idea of what is typically included in a Scene?

A Scene might include buttons, text fields, and images, right?

Absolutely! Scenes encompass all graphical elements such as nodes. Can anyone tell me what nodes are in this context?

I believe nodes are the actual components we interact with, like buttons and labels.

Yes! Nodes are essential as they form the interactive parts of a GUI. Can anyone summarize what we've learned so far?

We learned that the Stage is the main window, Scenes contain content, and Nodes are the interactive UI elements.

Great recap!
Putting it Together
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's put our understanding together. How do you think the Stage, Scene, and Nodes interact to create a JavaFX application?

The Stage presents a Scene that contains Nodes, right? So, it all starts with the Stage.

Exactly! Imagine the Stage opening up to a beautiful Scene filled with interactive Nodes. It’s like a play where everything unfolds on the Stage.

And if we want to change the story or content, we only need to change the Scene!

Right! Well summarized. Understanding this interplay helps in structuring our JavaFX applications clearly.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
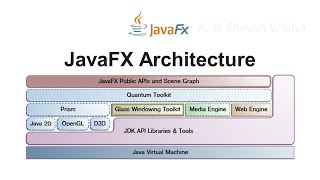
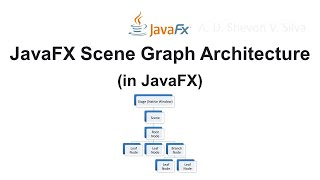
In JavaFX, the architecture is centered around three main components: the stage (the main window), the scene (the visual content within the stage), and nodes (UI components like buttons and labels). Understanding these components is essential for effective JavaFX GUI development.
Detailed
JavaFX Architecture
JavaFX represents a significant evolution in GUI programming within Java, featuring a comprehensive architecture designed to facilitate rich user interfaces. At the core of JavaFX architecture are three key components:
- Stage: This is essentially the main window of the application where all visual content is displayed. It acts as a top-level container that holds the various scenes.
- Scene: Each stage can contain one or more scenes. A scene encapsulates the visual content and layout, serving as the container for nodes, which comprise the interface elements.
- Nodes: These are the UI components such as buttons, labels, and other controls that the user interacts with. Nodes can be structured into scenes to create the overall user experience.
Understanding these components simplifies structuring and designing user interfaces in JavaFX, promoting a cleaner and more organized approach to GUI application development.
Youtube Videos



Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Stage: Main Window
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Stage: Main window.
Detailed Explanation
In JavaFX, the 'Stage' represents the main window of the application. Think of it as a theater stage where everything takes place. When you create a JavaFX application, the 'Stage' is the base where you can set up your application's user interface. Just like a theater stage can hold different scenes, the 'Stage' in JavaFX can contain different scenes that you can switch between.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you are watching a play. The stage is where the actors perform their scenes. Similarly, in a JavaFX app, the stage is where all the visual elements appear, like buttons, labels, and more. Without a stage, the performance (or application) wouldn't have a place to happen.
Scene: Content Inside the Window
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Scene: Content inside the window.
Detailed Explanation
A 'Scene' in JavaFX is what holds the visual elements that appear on the 'Stage'. You can think of a 'Scene' as a particular layout or set of components that fill the stage. Each scene can have its own unique layout, and you can change the scene according to how you want your application to look at different times. Scenes can contain everything from buttons to text boxes to images.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a theater play again: each scene of the play has specific props and actors that set the mood and context. Similarly, a Scene in JavaFX has specific components (like buttons and labels) organized in a way that serves a particular purpose in your app, whether it’s to gather user input or display information.
Nodes: UI Components
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Nodes: UI components (buttons, labels, etc.).
Detailed Explanation
In JavaFX, 'Nodes' are the building blocks of the user interface. Each component in a scene, such as buttons, labels, text fields, and images, is considered a 'Node'. Nodes are crucial because they are the items that users interact with. Each node can be manipulated (like changing colors, size, and behavior) to create a dynamic and responsive user interface.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a recipe where each ingredient represents a Node in the final dish. Just like each ingredient affects the taste and appearance of the dish, each Node influences how users interact with the application. Without Nodes, there wouldn't be anything for the user to click, type, or view on the screen.
Key Concepts
-
Stage: The main window of a JavaFX application.
-
Scene: Contains the visual content of a Stage.
-
Nodes: UI components that are part of a Scene.
Examples & Applications
A simple JavaFX application creates a Stage, adds a Scene with a button node, and displays it to the user.
Switching between different scenes on the same stage based on user input, demonstrating the flexibility of JavaFX.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In JavaFX's world, we've got Stage, / A Scene acts next in our visual page. / Nodes play their part, so bright and clear, / Together they build an interface we cheer!
Stories
Imagine a theater (Stage) where different plays (Scenes) occur. Each actor (Node) plays a role in creating the magic of the performance, with scenes changing as the audience desires.
Memory Tools
For remembering the components, think 'S-S-N': Stage, then Scene, finally Nodes
Acronyms
SNAP
Stage
Nodes
Action
Presentation - covers the essential parts of JavaFX architecture.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Stage
The main window of a JavaFX application that holds all the scenes.
- Scene
A container for the visual content displayed in a Stage, consisting of Nodes.
- Nodes
The individual UI components (like buttons, labels) that users interact with in a Scene.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
