Event Handling in GUI
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Event Sources
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're talking about event handling in GUI applications. Let's start with event sources. Can anyone tell me what an event source is?

Is it a component that creates events?

Correct! An event source is any GUI component that can generate an event, like buttons or windows. For example, when you click a button.

So, a button is an event source?

Exactly! Now, can someone explain why understanding event sources is important?

We need to know how to attach listeners to them so we can handle the events they generate!

Correct! Remember: **E.S.P.** - Event Source - Produces events! Great job, everyone!
Event Listeners
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Next, let's dive into event listeners. What do you think they do?

They listen for events generated by event sources!

Absolutely right! Can you name some common event listener interfaces?

Uh, ActionListener and MouseListener?

Great! And how about their primary functions?

ActionListener handles action events like button clicks, while MouseListener deals with mouse actions.

Exactly! Let's remember it with the mnemonic **A.M.** - Action for ActionListener and Mouse for MouseListener. Well done!
Lambda Expressions in Event Handling
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's talk about lambda expressions. Who can explain what they are in the context of event handling?

They simplify how we handle events in Java 8 and later versions.

Right! Instead of writing out a full class for an event listener, you can use a shorthand. Can anyone give me an example?

Like using this? `button.addActionListener(e -> System.out.println("Clicked!"));`

Perfect! That's much cleaner, isn’t it? Let’s use **L.E.S.S.** for Lambda Expressions Simplifying Syntax - easy to remember!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
In this section, we explore how GUI components in Java generate events and how these events are processed through various listener interfaces. We also delve into the use of lambda expressions for event handling, simplifying the coding process in Java 8 and later versions.
Detailed
Event Handling in GUI
Event handling is a crucial aspect of GUI programming, enabling interactive behavior in applications. In Java, GUI components like buttons and windows generate events, which are captured by listener interfaces to trigger specific actions. This section focuses on two main components:
- Event Sources: These are components that generate events, such as buttons, which, when clicked, can produce an action event.
-
Event Listeners: These are interfaces that define methods to handle different types of events. For instance, an
ActionListenerprocesses action events, while aMouseListenerhandles mouse-related events.
Additionally, with the introduction of Java 8, lambda expressions have provided a new syntax for handling events, enabling more concise and readable code. For example:
This not only streamlines event handling but also enhances the developer experience, making code easier to read and maintain.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Event Sources and Listeners
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Source: Component that generates an event (e.g., Button).
• Listener: Interface that processes the event (e.g., ActionListener, MouseListener).
Detailed Explanation
In GUI programming, an 'event' is an action that occurs due to user interaction, such as clicking a button or moving the mouse. These events are generated by GUI components, which are referred to as 'event sources.' For example, a button that a user clicks is an event source because it generates an event when clicked. On the other hand, an 'event listener' is an interface that listens and responds to these events. When you set up an event listener, you define what should happen when a specific event occurs, allowing your application to react to user interactions.
Examples & Analogies
Think of an event source as a microphone that picks up sounds (events) in a room. The listeners are like people in that room who respond to the sounds they hear. For instance, when a bell rings (an event from the microphone), a listener might start clapping because they know it's time to celebrate.
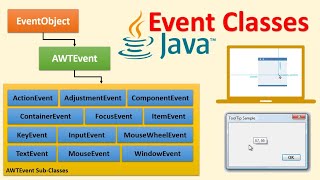
Common Event Listener Interfaces
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Button click: ActionListener
• Mouse events: MouseListener, MouseMotionListener
• Key press: KeyListener
• Window open/close: WindowListener
Detailed Explanation
In Java GUI programming, there are specific interfaces designed to listen for different types of events. For button clicks, the 'ActionListener' interface is used, which processes the action when a user clicks a button. For mouse movements and actions, you have 'MouseListener' and 'MouseMotionListener,' which handle the mouse events such as clicks, movements, and drags. You also have 'KeyListener' for responding to keyboard presses, and 'WindowListener' for detecting when a window is opened or closed. These interfaces allow you to effectively manage and respond to user actions in your applications.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you are at a concert where different band members play different instruments. Each musician has their own role (like 'ActionListener' for buttons, 'MouseListener' for mouse actions, etc.) and responds to the music (events) in unique ways, allowing the concert to be a coordinated experience.
Lambda in Event Handling (Java 8+)
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
button.addActionListener(e -> System.out.println("Clicked!"));
Detailed Explanation
With the introduction of Java 8, event handling was made even more concise using 'lambda expressions.' A lambda allows you to write implementations of interfaces in a more streamlined way. For instance, rather than writing a full class that implements ActionListener, you can use a lambda expression directly to define the action that should happen when a button is clicked. In the example provided, when the button is clicked, it will print 'Clicked!' to the console. This method reduces boilerplate code and makes it easier to write and read event-handling code.
Examples & Analogies
Consider cooking a dish where you usually follow a lengthy recipe step-by-step; using a lambda expression is like having a friend come in and just say, 'Add salt and stir!' instantly, focusing only on what matters without all the unnecessary details.
Key Concepts
-
Event Source: A component that generates events.
-
Event Listener: An interface to handle events.
-
ActionListener: Listens to button click events.
-
MouseListener: Listens for mouse actions.
-
Lambda Expressions: Modern syntax for event handling.
Examples & Applications
When a button is clicked, it generates an action event, which is handled by an ActionListener.
Using a MouseListener, we can respond to mouse hover events over a GUI component.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Event sources create, listeners activate, in the GUI world, that's how we relate.
Stories
Imagine a button named 'Press Me'; every time it’s clicked, it whispers to its listener, ‘I was pressed!’
Memory Tools
Remember L.E.S. - Listeners Ease Syntax when using lambda expressions.
Acronyms
Use **E.S.P.** - Event Source Produces events to recall event sources.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Event Source
A GUI component that generates events, such as buttons and windows.
- Event Listener
An interface in Java that processes events generated by event sources.
- ActionListener
An interface that handles action events, typically generated by buttons.
- MouseListener
An interface that reacts to mouse actions in the GUI.
- Lambda Expression
A concise way to represent an anonymous function that can be used to define event handlers in Java.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
