Event Handling in AWT
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Event Handling
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Welcome, class! Today we'll discuss event handling in AWT. Who can tell me what an event is in a GUI context?

An event is an action that occurs due to user interaction, like clicking a button.

Exactly! Events like button clicks, mouse movements, or key presses are essential as they trigger responses in your application.

How does Java handle these events specifically?

Good question! Java uses a delegation event model where components generate events and listeners handle them.
Understanding Listeners
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Listeners are the backbone of event handling. Can anyone name a common listener interface in Java?

ActionListener is commonly used for button clicks.

Correct! An ActionListener lets you define what happens when an action occurs, such as a button click. For example, here's a snippet of code that creates a button:

Button b = new Button("Click"); b.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {...});

So, when the button is clicked, it uses that listener to respond with a defined action?

Exactly! This separation allows for flexible and reusable code.
Event Generation and Handling
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's delve into event generation. What happens when a user clicks a button?

The button generates an event which the listener picks up.

That's right! The event object is passed to the listener's method where you can define your action. Can anyone suggest what happens if there's no listener?

If there's no listener attached, the event simply has no effect.

Exactly! A listener is crucial; without it, the event goes unhandled. Let's reinforce this with a quick summary of today's topic.
Practical Application Example
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

To visualize our learning, let's write a simple application. Imagine a button that prints 'Button clicked!' when pressed. How would we structure the code?

We create a button and attach an ActionListener that processes the click action.

Exactly! Here's how it looks in code: Button btn = new Button("Click Me"); btn.addActionListener(e -> System.out.println("Button clicked!"));

Oh, I see! So the 'e' is the event object?

Correct! Understanding this interaction is key to becoming proficient in GUI programming.
Summary and Key Takeaways
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

To wrap up, who can summarize what we've learned about event handling in AWT?

We learned that components generate events and listeners handle them using the delegation event model.

Correct! And remember the importance of attaching listeners to components for interactive functionality. They're critical in building responsive applications.

This makes it clear how crucial event handling is in GUI programming.

Absolutely! Great work today, everyone!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section discusses how event handling is crucial in AWT programming, focusing on the delegation event model where components generate events and listeners handle these events using interfaces like ActionListener.
Detailed
In this section of Chapter 16, we explore event handling within the Abstract Window Toolkit (AWT) in Java GUI programming. Event handling is based on the delegation event model, which separates the event generation process from event handling. In AWT, various components, such as buttons and text fields, can generate events. When a user interacts with these components, events are triggered, which are then handled by appropriate listeners. For example, the code snippet provided illustrates a button that triggers an action when clicked, showcasing how listeners like ActionListener can be used to define the behavior corresponding to the event. Understanding this model is essential as it allows developers to create responsive and interactive GUI applications.
Youtube Videos


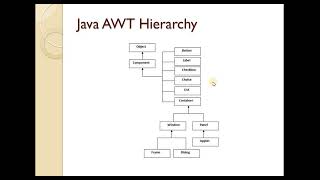






Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Overview of Event Handling in AWT
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Based on Delegation Event Model.
Detailed Explanation
AWT uses the Delegation Event Model for handling events. In this model, events are generated by components (like buttons), and instead of handling these events directly, we delegate the responsibility of handling to separate listener objects. This means that when an event occurs (like a button click), the component that generated the event will notify its associated listener, which contains the logic to respond to that event.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a waiter in a restaurant. When a customer orders food (the event), the waiter (the listener) takes the order and communicates it to the kitchen (the event's response). The waiter doesn’t cook the food; they pass the order to someone else who does. Similarly, in AWT, components pass events to their listeners.
Components Generate Events
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Components generate events.
Detailed Explanation
In AWT, various components like buttons, text fields, and checkboxes can generate events. For example, when a button is clicked, it generates an ActionEvent. Different types of components generate different types of events; for instance, a mouse click generates a MouseEvent, while typing in a text field generates a KeyEvent. Each of these events carries information about what happened, such as the type of event and the component that triggered it.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a doorbell at your home. When someone presses it (the event), it rings (the response). Different buttons can be thought of as different types of doorbells, each creating a distinct sound or action when pressed.
Listeners Handle Events
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Listeners handle them.
Detailed Explanation
Listeners are special objects in AWT that wait for events to occur and define what should happen when an event occurs. You add a listener to a component by calling a method like addActionListener, passing in the listener as an argument. The listener then implements an interface (such as ActionListener) with methods like actionPerformed, where you specify the actions to be taken when an event occurs. This separation of the event generation and handling logic promotes cleaner and more maintainable code.
Examples & Analogies
Continuing with the restaurant analogy, when an order is taken (event generation), the chef (listener) has a specific recipe (code) to prepare the food when the order comes in. The chef doesn’t decide how to take the order; they just focus on cooking the dish.
Example of Event Handling
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Button b = new Button("Click");
b.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
System.out.println("Button clicked!");
}
});
Detailed Explanation
In this code snippet, we create a Button object named 'b' with the label 'Click'. We then add an ActionListener to the button which listens for click events. When the button is clicked, the actionPerformed method is triggered, executing the code inside it, which prints 'Button clicked!' to the console. This is a simple example of event handling in AWT where an action performed by the user (button click) results in a specific behavior (printing a message).
Examples & Analogies
Think of a light switch. When you press the switch (event), it turns the light on (defined action). The button click in your code is like someone turning on the light, where the 'actionPerformed' method is defined to perform that action.
Key Concepts
-
Event Generation: The process where user interactions with components trigger events.
-
Listeners: Interfaces that handle events generated by components.
-
Delegation Event Model: A design structure where components handle event generation separately from event handling.
Examples & Applications
Button Action Example: When a button is clicked, it may generate an event that is processed by an ActionListener, typically to trigger a response such as printing a message.
Event Handling Code Snippet: Button b = new Button("Click"); b.addActionListener(new ActionListener() { public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) { System.out.println("Button clicked!"); } });
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
When you click a button, listen to its sound; ActionListener will respond, and joy will abound!
Stories
Imagine a busy cafe where each button on the counter signals a different order; the ActionListener is like the staff ready to respond to each order.
Memory Tools
Remember the acronym 'DEL' for Delegation, Event, and Listener in event handling.
Acronyms
A.L.E. - ActionListener, Generates Events, Listeners respond!
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Event
An action generated by a user interaction, such as clicking a button.
- Listener
An interface that receives and processes events triggered by components.
- ActionListener
A functional interface that receives action events, typically from buttons.
- Delegation Event Model
A design pattern where event sources generate events and listeners handle them separately.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
